What are the symptoms of sebaceous cysts?
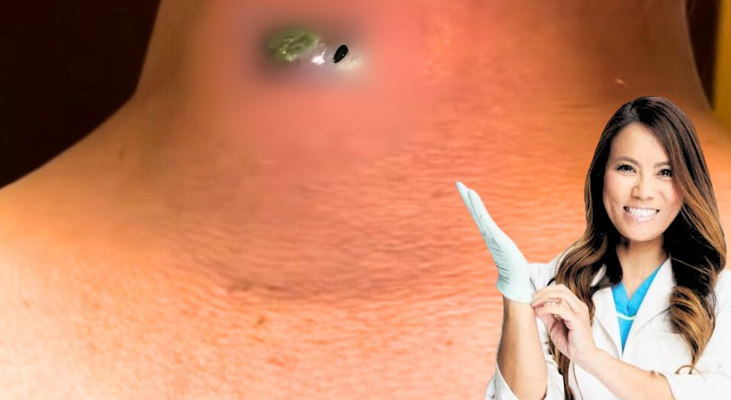
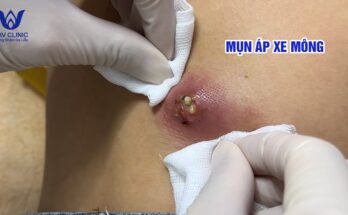
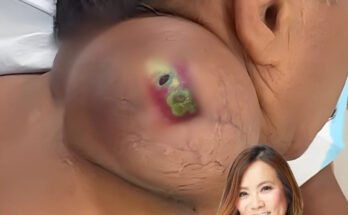
The presence of a lump or growth under the skin is usually a sign that you may be developing a sebaceous cyst. Sebaceous cyst may initially appear soft, but later grow firmer as the amount of keratin builds up in the wall of the cyst. Most cysts are benign and completely harmless. At the start, the the cyst is painless, but depending on the location of the cyst, it can become irritated, erythematous, and inflamed. This inflammation can be a sign of an underlying skin infection. If the cyst becomes tender to the touch and the surrounding skin appears red and warm, the sebaceous cyst may be infected, and will need further treatment. The cyst may need to be opened and drained, allowing the infection to escape, and oral antibiotics will need to be prescribed. When the cyst becomes painful, or the surrounding skin becomes warm with a foul smelling discharge, this is a strong indication of infection. In an infection is left untreated, it can become serious. Fever, or any other systemic symptoms means that prompt medical attention is necessary.
While most sebaceous cysts pose no cancerous threat it cannot be ruled out entirely. A sebaceous cyst may be considered abnormal or possibly cancerous if it’s diameter is larger than five centimeters, or continues to recur in the same location after repeatedly being removed.
How do you diagnose a sebaceous cyst?
A diagnosis of a sebaceous cyst can be determined by a physical examination of the nodule by a dermatologist, family physician or other healthcare provider. There are occasions when additional testing is required to make a definitive diagnosis of a cyst, since it can sometimes be mistaken for a different type of skin tumor.
Common tests used to diagnosis a sebaceous cyst include:
- Cat scan – This test is performed to rule out other abnormalities or cancer.
- Ultrasound – This test is performed to establish the contents of the cyst and depth of inflammation.
- Punch biopsy – This test is performed to identify the histology of the cyst.
- Culture and Sensitivity – This exam is performed to determine the type of bacteria responsible for the infection and the best antibiotic to treat the infection.